Basically it Allows Braking and Steering
Also known as anti skid brakes, modern ABS systems electronically monitor the speed of the wheels and regulate the hydraulic pressure accordingly. The aim is to maximize braking power while preventing the wheels from locking and skidding.By keeping the wheels from skidding while you slow down, anti-lock brakes benefit you in two ways: You’ll stop faster, and you’ll be able to steer while you stop.
IMPORTANT :
ALL THOSE WHO OWN OR DRIVE VEHICLES WITH “ABS” PLEASE NOTE
- While operating a vehicle with ABS never pump the brakes. Doing so will make the ABS system ineffective. Always apply firm pressure.
- Drivers may experience a pulsation/vibration in the brake pedal, or pedal kick back during an ABS stop. This is normal and not to be confused with a conventional brake pedal pulsation along with a buzzing sound
- ABS system can maintain extremely high static pressure and must be disabled before attempting repairs. Normally pumping brake 20-30 times will release pressure
Based on studies made by insurance institute of road safety (IIHS) to determine if cars equipped with ABS are involved in more or fewer fatal accidents, vehicles equipped with ABS were overall no less likely to be involved in fatal accidents than vehicles without. The study actually stated that although cars with ABS were less likely to be involved in accidents fatal to the occupants of other cars, they are more likely to be involved in accidents fatal to the occupants of the ABS car, especially single-vehicle accidents.
The reason for this is that some people think that drivers of ABS-equipped cars use the ABS incorrectly, either by pumping the brakes or by releasing the brakes when they feel the system pulsing. Some people think that since ABS allows you to steer during a panic stop, more people run off the road and crash.
- Integrated :An integrated system has the master cylinder and control valve assembly made together.
- Non integrated: A non integrated has the master cylinder and control valve assembly made separate
Four main components of an ABS system:
- Speed sensors
- Pump
- solenoid Valves
- Controller
Speed Sensors
The anti-lock braking system needs some way of knowing when a wheel is about to lock up. The speed sensors, which are located at each wheel, or in some cases in the differential, provide this information.
Valves
There is a valve in the brake line of each brake controlled by the ABS. On some systems, the valve has three positions:
- In position one, the valve is open; pressure from the master cylinder is passed right through to the brake.
- In position two, the valve blocks the line, isolating that brake from the master cylinder. This prevents the pressure from rising further should the driver push the brake pedal harder.
- In position three, the valve releases some of the pressure from the brake.
Pump
Since the valve is able to release pressure from the brakes, there has to be some way to put that pressure back. That is what the pump does; when a valve reduces the pressure in a line, the pump is there to get the pressure back up.
Controller
The controller is a computer in the car. It watches the speed sensors and controls the valves. It controller monitors the speed sensors at all times. It is looking for decelerations in the wheel that are out of the ordinary. Right before a wheel locks up, it will experience a rapid deceleration. If left unchecked, the wheel would stop much more quickly than any car could. It might take a car five seconds to stop from 60 mph (96.6 kph) under ideal conditions, but a wheel that locks up could stop spinning in less than a second.
The ABS controller knows that such a rapid deceleration is impossible, so it reduces the pressure to that brake until it sees an acceleration, then it increases the pressure until it sees the deceleration again. It can do this very quickly, before the tire can actually significantly change speed. The result is that the tire slows down at the same rate as the car, with the brakes keeping the tires very near the point at which they will start to lock up. This gives the system maximum braking power.
When the ABS system is in operation you will feel a pulsing in the brake pedal; this comes from the rapid opening and closing of the valves. Some ABS systems can cycle up to 15 times per second.
Anti-lock Brake Systems (ABS) working
When the brakes are applied, fluid is forced from the brake master cylinder outlet ports to the HCU(hydraulic control unit) inlet ports. This pressure is transmitted through four normally open solenoid valves contained inside the HCU, then through the outlet ports of the HCU to each wheel.The primary (rear) circuit of the brake master cylinder feeds the front brakes.
The secondary (front) circuit of the brake master cylinder feeds the rear brakes.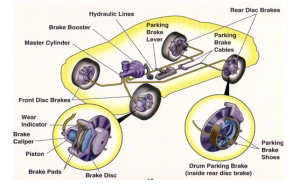

If the anti-lock brake control module senses a wheel is about to lock, based on anti-lock brake sensor data, it closes the normally open solenoid valve for that circuit. This prevents any more fluid from entering that circuit.The anti-lock brake control module then looks at the anti-lock brake sensor signal from the affected wheel again.If that wheel is still decelerating, it opens the solenoid valve for that circuit.Once the affected wheel comes back up to speed, the anti-lock brake control module returns the solenoid valves to their normal condition allowing fluid flow to the affected brake.The anti-lock brake control module monitors the electromechanical components of the system.Malfunction of the anti-lock brake system will cause the anti-lock brake control module to shut off or inhibit the system. However, normal power-assisted braking remains.Loss of hydraulic fluid in the brake master cylinder will disable the anti-lock system. The 4-wheel anti-lock brake system is self-monitoring. When the ignition switch is turned to the RUN position, the anti-lock brake control module will perform a preliminary self-check on the anti-lock electrical system indicated by a three second illumination of the yellow ABS wanting indicator.During vehicle operation, including normal and anti-lock braking, the anti-lock brake control module monitors all electrical anti-lock functions and some hydraulic operations.Each time the vehicle is driven, as soon as vehicle speed reaches approximately 20 km/h (12 mph), the anti-lock brake control module turns on the pump motor for approximately one-half second. At this time, a mechanical noise may be heard. This is a normal function of the self-check by the anti-lock brake control module.
When the vehicle speed goes below 20 km/h (12 mph), the ABS turns off.
Most malfunctions of the anti-lock brake system and traction control system, if equipped, will cause the yellow ABS warning indicator to be illuminated.
WATCH IT IN REAL ACTION(If your really busy just switch to 1:05)
Do follow us for more interesting article




